News & Media

A New Look, Same Commitment: Welcome to the New GMFS
Today, we’re proud to introduce a refreshed brand that better reflects who we are, what we stand for, and where we’re going.

GMFS Mortgage Macon Voted Best Home Mortgage 2025
GMFS Mortgage’s Macon, GA branch has been voted as the 2025 Best Home Mortgage Company - AGAIN! Contact our award-winning team today!

Which Down Payment Assistance Programs Are Available to You?
Down payment assistance can help you buy a home sooner than you think. Connect with GMFS Mortgage to find the best program for your needs.

2 GMFS Mortgage Loan Officers named to Scotsman Guide 2025 Top Female Originators List
We are thrilled to announce that Stephanie Machado Barto and Aimia Doucet, esteemed Loan Officers at GMFS Mortgage, have been recognized among the top female mortgage originators in the nation by Scotsman Guide's 2025 Top Women Originators ranking list.

While a fixed-rate mortgage locks in your interest rate for the life of the loan, an ARM offers an interest rate that adjusts over time.

What Is a Self-Build Construction Loan?
A self-build construction loan is designed for borrowers who want to manage the construction of their new home themselves, rather than hiring a general contractor to handle the entire project. With this type of loan, you work directly with builders and subcontractors, and take responsibility for coordinating and managing the overall process.
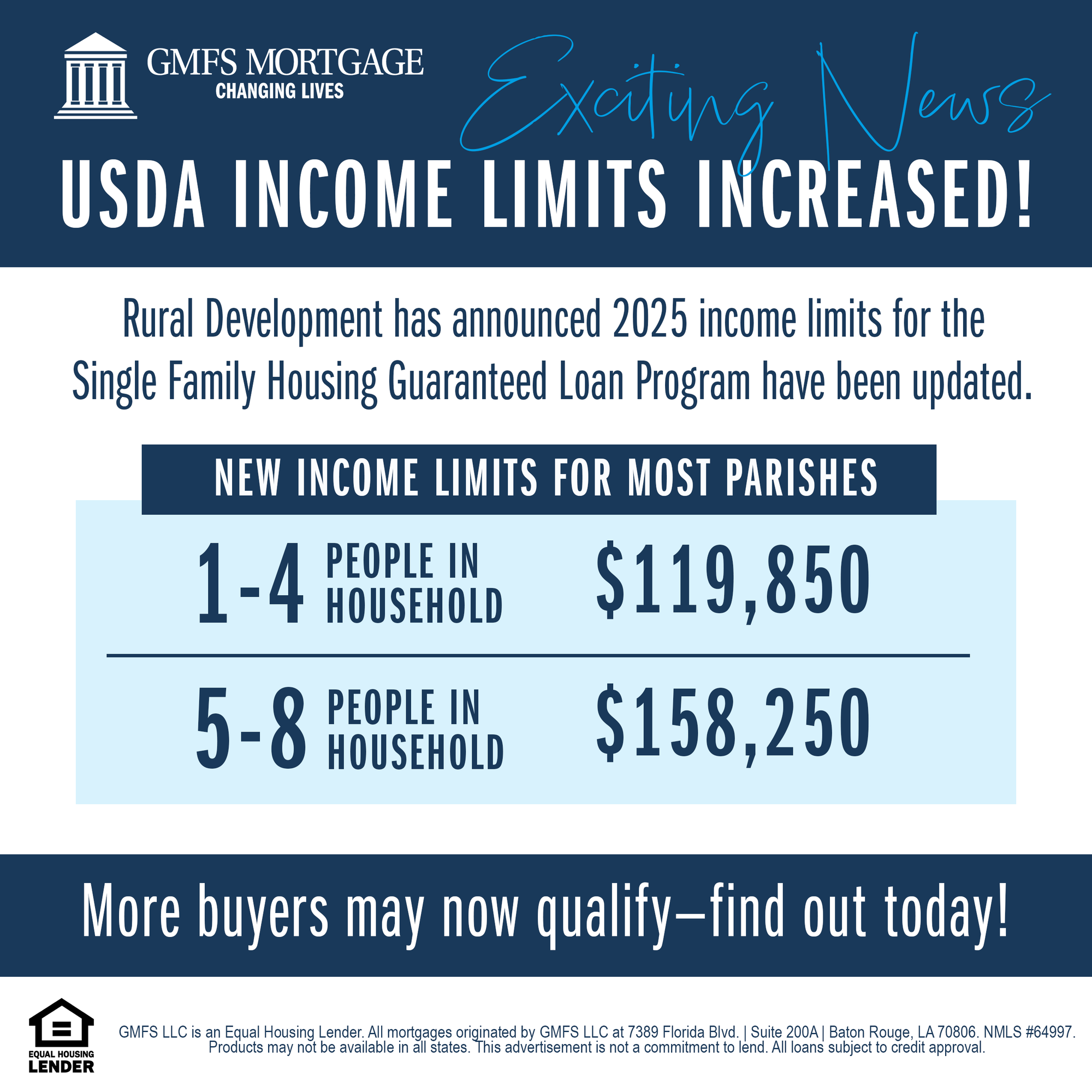
USDA Rural Development Income Limits 2025
USDA Rural Development increased Income Limit for the Single Family Guaranteed Loan Program in 2024. Get pre-qualified today!